Observation Notes
Pickering's Triangle
The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus.
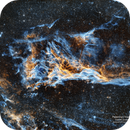
Pickering's Triangle
 *Pickering's Triangle from Everett Quebral's AstroBin gallery*
*View on AstroBin: [https://app.astrobin.com/i/zavxuw](https://app.astrobin.com/i/zavxuw)*
*Pickering's Triangle from Everett Quebral's AstroBin gallery*
*View on AstroBin: [https://app.astrobin.com/i/zavxuw](https://app.astrobin.com/i/zavxuw)*
About Pickering's Triangle
Learn more about Pickering's Triangle on Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Veil_Nebula
What Creates the Appearance
We see shock fronts from the ancient supernova plowing into surrounding gas. Oxygen-III glows a teal/blue where fast shocks excite doubly ionized oxygen; hydrogen-alpha reveals red, threadlike filaments. The geometry and magnetic fields create the intricate lacework.
The Science Behind the Beauty
Pickering's Triangle is part of the Cygnus Loop, the expanding debris of a massive star that exploded thousands of years ago. As the blast wave sweeps through the interstellar medium, it compresses, heats, and ionizes gas, which then cools and radiates in characteristic emission lines.
Capturing the Target
Equipment and Setup
- Telescope/Optics: Explore Scientific 127mm ED APO Triplet with 0.7× reducer; Orion ED80T CF APO Triplet (earlier sessions)
- Imaging Camera: ZWO ASI1600MM-Cooled
- Filters: Astronomik Hα 12 nm, Astronomik O III 12 nm
- Mount: Orion Atlas EQ-G
- Guiding: Autoguiding with ZWO ASI120MM-S
Imaging Strategy
For this field, a bicolor HOO approach (Hα and [O III]) works well. Collect many long sub-exposures and balance total integration across channels to manage SNR. Typical total integration from this dataset: 20h 48m. Image resolution: 1824×1569.
Processing Techniques
- Calibration: Apply darks, flats, and biases
- Registration & Integration: Align and stack frames
- Channel Combination: Map SII/Ha/OIII into palettes (e.g., Hubble palette)
- Color Calibration: Balance narrowband colors while preserving structure
- Stretching: Gradual histogram stretches to reveal faint structure
- Detail Work: Noise reduction, deconvolution, and local contrast
The Surrounding Region
This target often sits within a rich region of gas, dust, and star-forming activity. Wide fields can capture multiple catalog objects, dark nebulae, and star clusters in the same frame.
Challenges and Rewards
- Faint Structure: Demands long total integration time
- Light Pollution: Narrowband can help under bright skies
- Weather & Seeing: Stable conditions improve small-scale detail
Tips for Success
- Plan sessions across multiple nights to build SNR
- Balance narrowband channels and manage star sizes across filters
- Use masks to protect stars and highlight nebular structure
- Keep a non-destructive workflow for iterative refinement
Conclusion
A delicate web of shock fronts and emission lines makes Pickering's Triangle a rewarding narrowband target, revealing exquisite structure with sufficient integration and careful processing.
Technical Data
- Object: Pickering's Triangle
- Constellation: Cygnus
- Integration: 20h 48m
- Resolution: 1824×1569 px
- Filters used: Hα, O III
Equipment
Imaging Equipment
- Optics: Explore Scientific 127mm ED APO Triplet + 0.7× Reducer; Orion ED80T CF APO Triplet
- Camera: ZWO ASI1600MM-Cooled
- Mount: Orion Atlas EQ-G
- Filters: Astronomik Hα 12 nm, Astronomik O III 12 nm
- Accessories: EQ Focuser
- Software: PixInsight 1.8 Ripley
Guiding Equipment
- Guide Camera: ZWO ASI120MM-S
- Mount: Orion Atlas EQ-G
- Accessories: EQ Focuser